Monitor ghosting is an effect on an LCD flat panel display that occurs when a “ghost” image which was previously displayed continues to remain on screen even though part of the visual has changed. It is caused by smearing or blurring of the pixels.
Ghosting happens because of slow response time and the monitor’s inability to stay up to speed with the refresh rate. Many other issues are like ghosting that may occur which include screen tearing, input lag, stuttering, flickering, or runt frames.
These may or may not happen in combination with the ghosting effect. But in the event, you see an image in the present that was recently displayed in the past playback loop; you are probably experiencing a ghosting effect. This guide should help you identify the issues causing these adverse visual effects and list the corresponding solutions to mitigate them.
Use the OSD menu
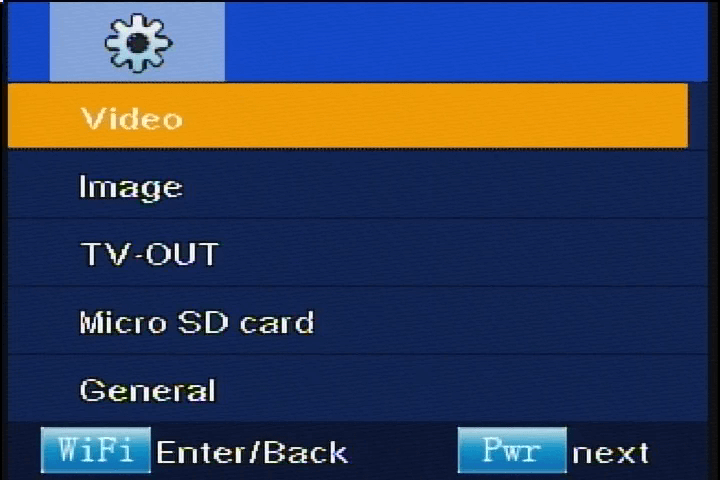
If you are using a stand-alone monitor with an on-screen display and not a laptop then follow these recommendations:
- Go to picture settings
- Scroll to and press AMA settings.
- Switch from the high setting to the medium setting or turn off this option altogether.
AMA stands for advanced motion acceleration, and it is part of response time compensation technology. Sometimes it is called ‘Overdrive.’ You may or may not know that LCD monitors moderate light flow by switching around liquid crystal molecules to different alignments where they produce and transfer different levels of light.
And the speed at which these molecules switch can be less than the monitor’s refresh rate. As a result, in a visual scenario such as a puck thrusting from the blade of a hockey stick, you will notice that the object is blurry.
This is because the overdrive technology is sending a high voltage to the pixels to give off enough energy to de-blur the picture as fast as possible. In an ideal situation, the AMA would be useful in reducing the ghosting, but if there is a discrepancy between the refresh rate and the response time, you will experience the adverse visual effects. Gaps between the graphics card and the monitor can also cause AMA to work inefficiently.
Why does response time acceleration or overdrive have different names?
The reason behind different manufacturers has different names for the same technology whether you decide to call it overdrive, excellent motion acceleration, response time compensation, or response time acceleration dates back to the inventor of the technology Robert Hotto of Positive Technologies.
Hotto had a patent issued when he developed the response time compensation technology that was copied by a large number of LCD manufacturers. The manufacturers simply renamed the technology feature to avoid paying royalties to Positive Technologies.
A lawsuit was filed against companies such as BenQ, Samsung, Sharp, NEC, LG and more. The lawsuit was won, and while the companies pay royalties to Positive Technologies, the naming of the feature did not change to a uniform one among the industry.
Conclusion
You can also access the response time menu and toggle between the options to find the best setting. The goal is to synchronize the response time with the refresh rate. If you still require better performance, you may want to opt to purchase a FreeSync monitor if you have an AMD graphics card or a G-Sync monitor if you have an NVIDIA graphics card. These can eliminate the effects of ghosting because they actively work to target the issue of synchronization between refresh rate and response time.
If you found this article helpful or require further help from us to clear up the issue of how to fix monitor ghosting, please use our support system via the comments section and Anthony will respond to you as soon as possible.
2 thoughts on “How to Fix Monitor Ghosting”
Comments are closed.